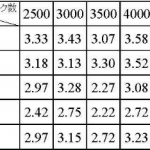
This study aimed to predict future changes in medical expenditures and examine regional disparities using machine lerarning models.
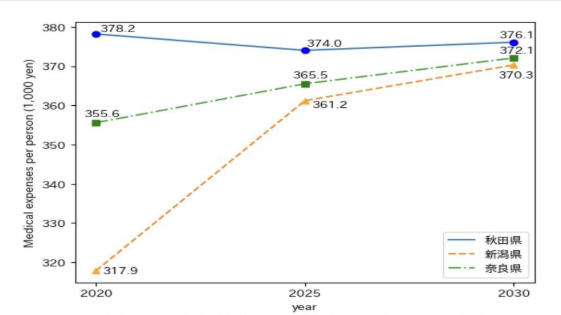
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare [1], three prefectures—Akita, Niigata, and Nara—were analyzed. Among several machine learning models tested, the Random Forest algorithm demonstrated the highest predictive accuracy. The results indicated a slight decrease in medical expenditures in Akita Prefecture, while expenditures were projected to increase in Niigata and Nara Prefectures. Akita showed progress in home-based medical care; Niigata exhibited slower development in healthcare infrastructure; and Nara, despite having many medical facilities, had a relatively low rate of health checkup participation.
These findings highlight the importance of promoting region-specific healthcare initiatives tailored to local characteristics.

[1] Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare: National Health Expenditures: Summary of Results, https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/list/37-21c.html, (Accessed 2023-06-05).