In this study, we investigated the quality of programs automatically generated by large language model (LLM) by applying code metrics—such as the number of code steps and complexity—and static analysis tools. In recent years, LLMs represented by ChatGPT have demonstrated strong capabilities in programming support, and their use is expected to contribute to improvements in development efficiency and maintainability. However, automatically generated code may contain unnecessary variables or conditional statements, and the current level of research on the quality of such code remains insufficient.
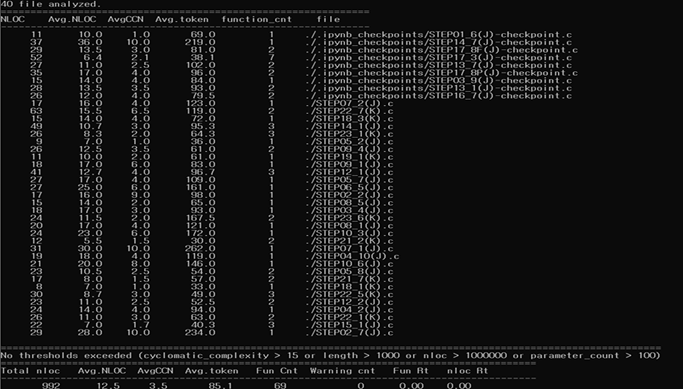
To address this issue, we asked ChatGPT to generate 40 C language programming problems and analyzed the resulting source code using the static analysis tool Lizard to evaluate its cyclomatic complexity (CCN).
| CCN | Guideline |
| 1~10 | Simple and easy-to-understand program. |
| 11~20 | Moderately complex program. |
| 21~ | Highly complex program; difficult to fully understand and to create comprehensive tests. |
| 50〜 | Very difficult to maintain; a program in which latent bugs are almost certain to exist |
The results showed that 32 out of the 40 programs were correct, yielding an accuracy rate of 80%. Furthermore,all code has a low complexity with a CCN value of 10 or below, indicating low complexity and high readability. Based on these findings, automatic programming using LLMs is expected to offer numerous benefits, including improved development speed, enhanced quality, increased maintainability, and reduced costs.